Google Analytics 4: Guide for your E-commerce Store

You might already be aware that Google Analytics 4 (GA4) has replaced Universal Analytics (UA) starting July 1, 2023. Since we all are gearing up to be accustomed to GA4 tracking as soon as possible, we have compiled some points that might help you. Starting from the integration process to combat tracking issues that arise, we have tried our best to address common concerns we came across.
Let’s get started:
Google Analytics 4 Integration
The first step to getting acquainted with GA4 property is implementing it on your online store. Google Analytics 4 collects event-based data from both websites and apps. If you are a Shopify merchant and have not integrated it yet, kindly complete the integration process to keep up with the updates.
Difference between Universal Analytics (UA) and Google Analytics 4 (GA4) tracking
As you prepare for Google Analytics 4, you might compare it against Universal Analytics. Based on this, one common concern that most merchants come forward with is that the data they had in UA doesn’t match the ones they see in the GA4 setup. It happens because there are differences in how Universal Analytics (UA) and Google Analytics 4 (GA4) track and report data. These points help you understand what to compare and what not to compare.
– Session Definition
Universal Analytics (UA) uses a session-based data model, grouping user interactions into sessions based on a 30-minute inactivity timeout or the end of the day. Google Analytics 4, on the other hand, uses an event-based data model, which means that it collects and analyzes individual user events across multiple sessions.
For example, in UA, if a user visits your store at 11:00 am and leaves at 11:15 am, that counts as one session. If the same user visits your store again at 11:45 am and leaves at 12:00 pm, that counts as another session. While in GA4 tracking, if the same user returns to your website at 11:45 am and leaves at 12:00 pm, that counts as the same session.
UA may define a session as a single visit from a single user, whereas GA4 may define a session as a sequence of visits from the same user.
– User Identification
UA uses a cookie-based method to identify users. It assigns a Client ID to each user’s browser or device and stores it in a cookie. GA4 uses a hybrid method to identify users. Along with a Client ID, it also uses other signals, such as Google signals, User ID, and Device ID, to enhance user identification and measurement. Due to this, the number of users reported by UA and GA4 may not tally.
– Bounce Rate/Engaged Sessions
In UA, a bounce rate is based on single-page sessions. For example, if a user visits your homepage and leaves without clicking on any links or buttons, that counts as a bounce.
Whereas in GA4, the bounce rate is based on engaged sessions. A session becomes a bounce if it meets all of the following criteria:
- It was less than 10 seconds long
- It had zero conversion events
- It had less than 2 page views
For example, if a user visits your homepage, scrolls down for 3 seconds, and leaves without clicking any links or buttons, that counts as a bounce. However, if the user stays on your homepage for more than 10 seconds, clicks on a link or a button, or views another page, that does not count as a bounce.
– Conversion Tracking
In Universal Analytics, a conversion is tracked by setting up a particular Goal. Each goal would correspond to specific user actions that you consider valuable, such as completing a form or making a purchase.
On the other hand, GA4 handles conversions through the use of ‘Events.’ Instead of setting up Goals, you mark specific Events as conversions. They can be anything from page views and button clicks to playing a video or completing a purchase.
It’s important to note that these differences do not mean one system is better or worse. It’s just that each of them uses a different methodology to help you understand your users and their interactions with your online store.
Link Google Ads and Google Analytics 4 property
Do we need to link Google Ads and Google Analytics 4?
Linking Google Ads and Google Analytics 4 allows a comprehensive understanding of your advertising efforts and user behavior. Linking them will let you view the clicks, impressions, and expenses recorded in your Google Ads account in your GA4 account. Simultaneously, user interaction, events, and conversions tracked in your GA4 can be fed into your Google Ads account.
It gives you deeper insights for analysis and enables more precise audience targeting and remarketing capabilities. It allows you to optimize your ad campaigns based on user behavior tracked by GA4, thus improving the effectiveness and return on investment.
To link them, you must have at least an Editor role in Analytics and administrative access in the Google Ads account. Then, you can follow these steps:
- In Google Analytics, click Admin (Make sure you are in the correct account and property)
- Scroll down to PRODUCT LINKS, and click Google Ads Links.
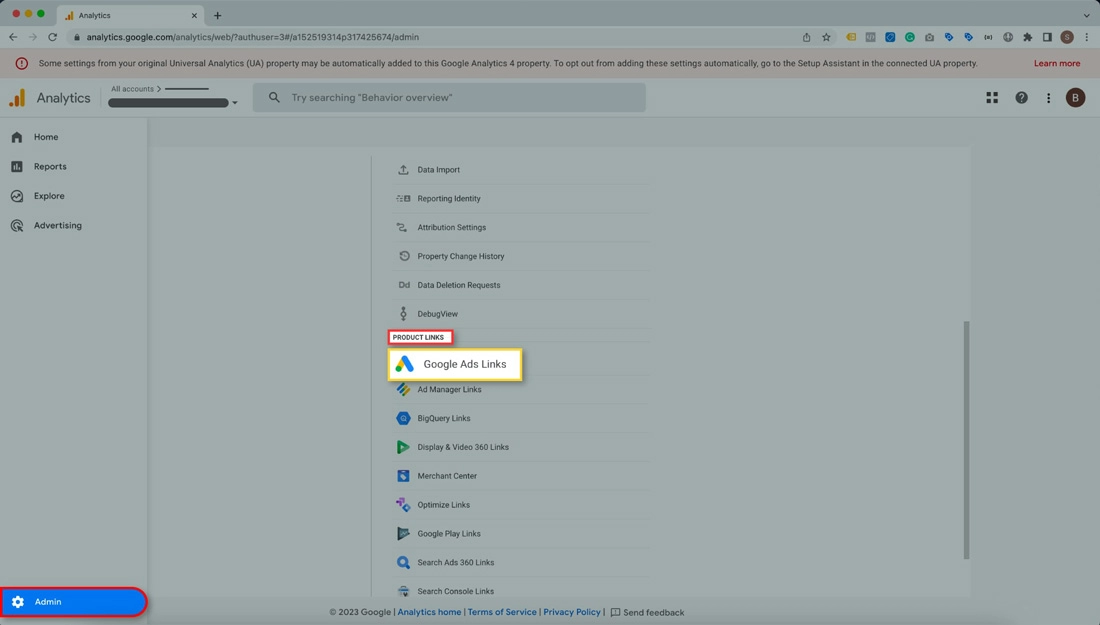
- Click on Link and then on Choose Google Ads accounts
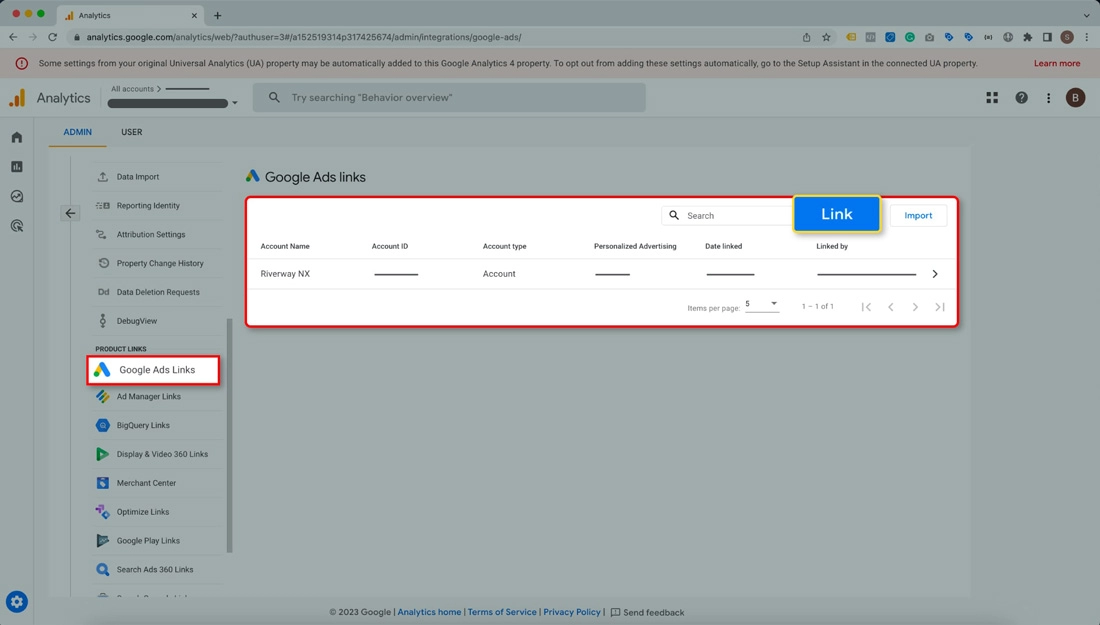
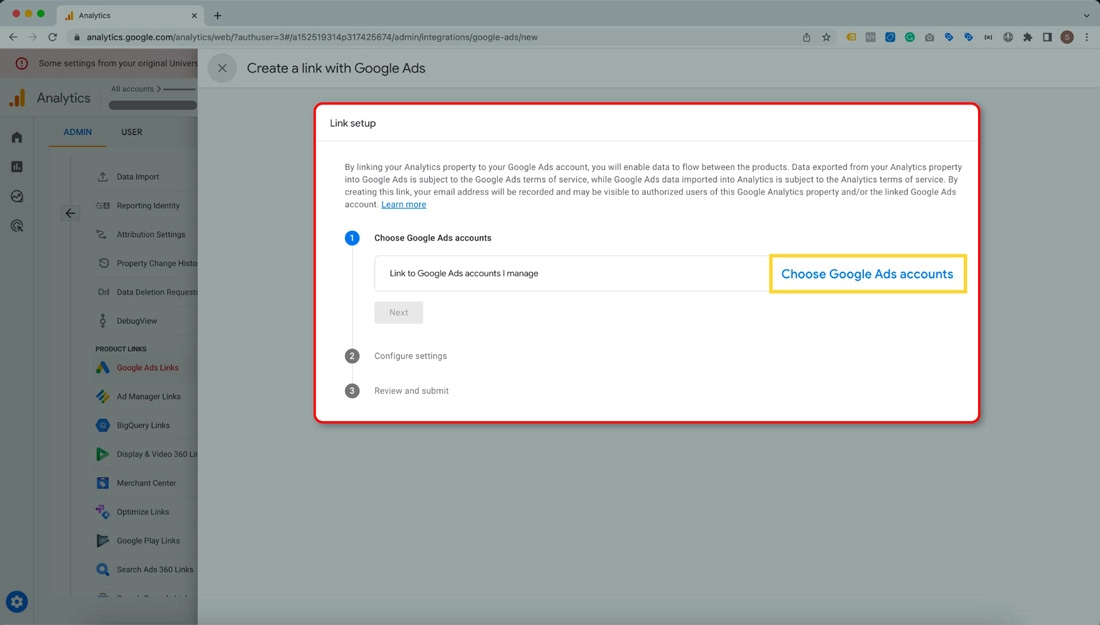
- Now, Choose the Google Ads accounts you want to link and click on Confirm.
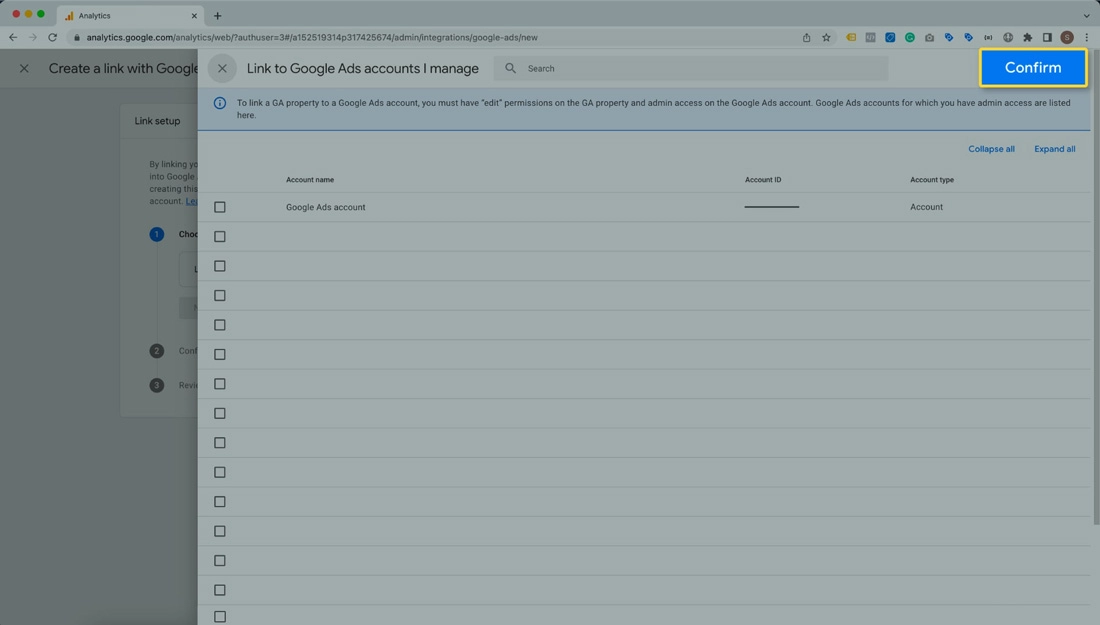
You can also link Google Analytics 4 in the Google Ads interface and import conversions.
Once linked, GA4 will start collecting additional data about how users interact with your website after clicking on your ads. Remember to ensure your privacy settings, cookie usage, and user agreements are compliant with all relevant regulations when sharing data between platforms
Google Analytics 4 events tracked through our app
For all those who have implemented the Google Analytics 4 property from our app Simprosys Google Shopping Feed, we have listed below the events tracked through our app.
– Search
This event is generated when a user performs a search action on the online store. It helps in tracking how users interact with the search functionality and can provide insights into the search feature’s efficiency.
– View_item_list
When a user views a list or collection of products, the view_item_list event is triggered. It is commonly used to track when a user views a page that has a list of products, such as a collection page or a search results page.
– View_item
When a user visits a specific item or product information page, this event is triggered. It indicates which products or items people are interested in and may assist in the analysis of user preferences and engagement with certain products.
– Add_to_cart
This event occurs when a user adds a product(s) to their shopping cart. It is often triggered when a user clicks on the “Add to Cart” button or performs a similar action.
– View_cart
When a user views their shopping cart, the view_cart event takes place. It usually occurs when a user returns to the cart page to review the products they have added before proceeding to the checkout process.
– Begin_checkout
This event occurs when a user begins the checkout process. It indicates that the user has moved on to the next step after adding products to the cart and is starting the process of purchasing the products.
– Purchase
When a user successfully completes a purchase, the purchase event is fired. It means a transaction has occurred and provides information such as the transaction ID, revenue, and other related details.
These events are used to analyze user behavior, understand conversion funnels, and improve store performance.
Setup Incomplete notification in the Google Analytics account
After completing the migration, you might still see one or both of the following notifications on your Google Analytics account:
“This property’s setup is not complete. Settings may be completed for you based on your original Universal Analytics (UA) property unless you opt out in the connected UA property.”
OR
“Some settings from your original Universal Analytics (UA) property may be automatically added to this Google Analytics 4 property. To opt out of adding these settings automatically, go to the Setup Assistant in the connected UA property.”
We have explained the step-by-step instructions to rectify this error. Kindly follow the steps and your Google Analytics account will stop showing the error.
Note: You might need to wait for a while after completing the steps as it takes time for the notifications to disappear.
Duplicate Google Analytics 4 Tags
Sometimes, you may see unusually high data recorded in your GA4 property. This could be due to duplicate events that can occur for various reasons. It may include technical issues, improper implementation, or user interactions that unintentionally trigger the same event multiple times.
These duplicate events can result in inaccurate and unreliable data tracking. It’s essential to ensure that you have only one GA4 tag implemented correctly to obtain accurate analytics data.
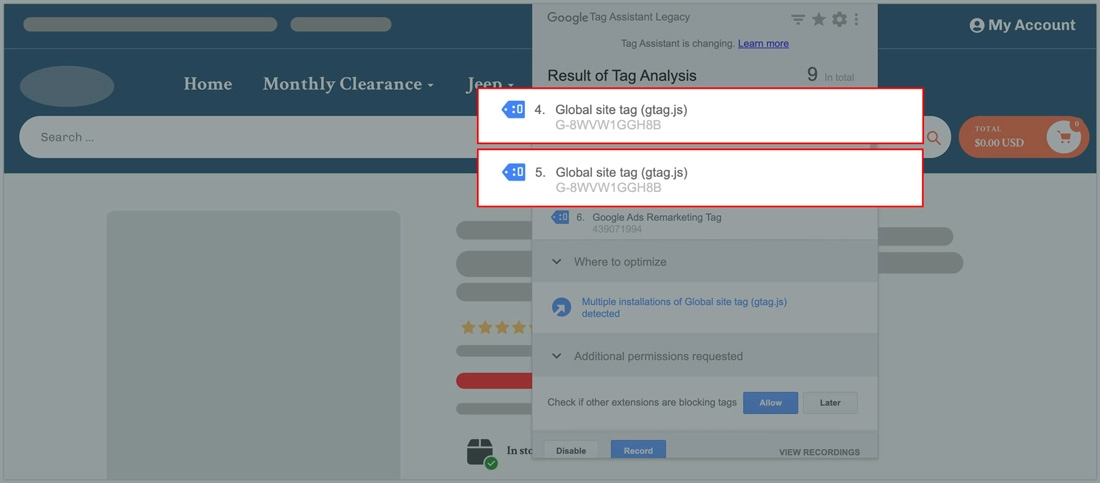
Here’s what you should do to address multiple/duplicate GA4 tags:
– Identify the duplicate tags
Verify your website’s GA4 tag with a tag management system, like Google Tag Assistant (if you’re using one) to find duplicate GA4 tags. You can also look for GA4 tracking code snippets.
– Remove the duplicate tags
Once you’ve identified the duplicate tags, remove them from your website. To prevent any conflicts or tracking discrepancies, it is essential to remove the entire GA4 tracking code snippet. Further, if you have enabled the tracking from multiple sources, you will have to disable them.
– Test and validate
After removing the duplicate tags, test your website to ensure that the GA4 tag appears only once. You can use Google Analytics Real-Time reports to verify that the tracking is functioning correctly and capturing data accurately.
– Update tag management systems
If you’re using a tag management system (such as Google Tag Manager), please remove the duplicate GA4 tags from there as well. Publish the changes and verify that the tag management system is correctly implementing the GA4 tag.
– Monitor data accuracy
After removing duplicate GA4 tags, monitor the information on your Google Analytics reports to ensure that the data is being tracked correctly. Verify important metrics and events to ensure they match up with your goals.
By following the above steps, you should be able to rectify the issue of multiple/duplicate GA4 tags on your website and ensure accurate tracking of your analytics data.
Tracking Issues in Google Analytics 4
After the GA4 setup is complete when you start analyzing your data, there are chances you might see that there is improper tracking of data. There could be discrepancies in the way the data is recorded. Here are some of the possible reasons:
– Incorrect Implementation
This is one of the most common reasons for improper tracking. Mistakes can happen at any stage of the setup process, from the tracking code placement to event configurations. Kindly make sure you have correctly implemented the GA4 tracking property. Further, GA4 uses an event-based tracking system, and if events are not properly set up or are missing, this can lead to gaps in the data.
– Different Data Processing
As mentioned above, GA4 processes data differently from Universal Analytics (UA). If you’re comparing GA4 data to UA data, it might appear as though GA4 is not tracking correctly when in fact it’s just using a different methodology. Because of the differences in how data is processed and categorized, you may notice significant differences when you compare data from UA and GA4. It’s not necessarily a problem with tracking; it’s a result of the different methodologies used by the two systems.
– Changes in Privacy Regulations
With the evolution of user privacy norms, more users are opting out of tracking or using browsers and extensions that limit tracking. If your users are heavily privacy-focused, this could impact your data. For example, Apple devices running the latest iOS versions require apps for permission to track users across apps and websites owned by other companies. Enabling the privacy settings in your Apple devices may affect the collection by GA4 property. The same goes for the GDPR in certain countries as they are also privacy-centric.
– Cookie Consent
Cookie consent mechanisms can significantly impact the data collected by Google Analytics 4 (GA4). Some websites obtain explicit cookie consent from users, including the ones used by GA4 for tracking. When a user does not accept cookies, GA4 cannot set or read cookies for that user, meaning it can’t collect data about the user’s behavior. This could lead to a decrease in reported users, sessions, and other metrics. Moreover, GA4 may also have difficulty accurately associating multiple sessions or events with the same user.
– Ad Blockers
Many ad blockers also block analytics trackers, including GA4. When a user has installed an ad blocker that blocks GA4, their activity will not be reported to GA4, resulting in potentially significant gaps in your data.
Therefore, it’s essential to keep them in mind when interpreting your GA4 data.
– Data Thresholding
It is a process designed to protect end-user privacy. If a specific combination of dimensions in your report does not meet a certain minimum threshold of sessions or users, Google will not display the data for that combination. Google uses data thresholding to prevent anyone from being able to identify individual users in your analytics data.
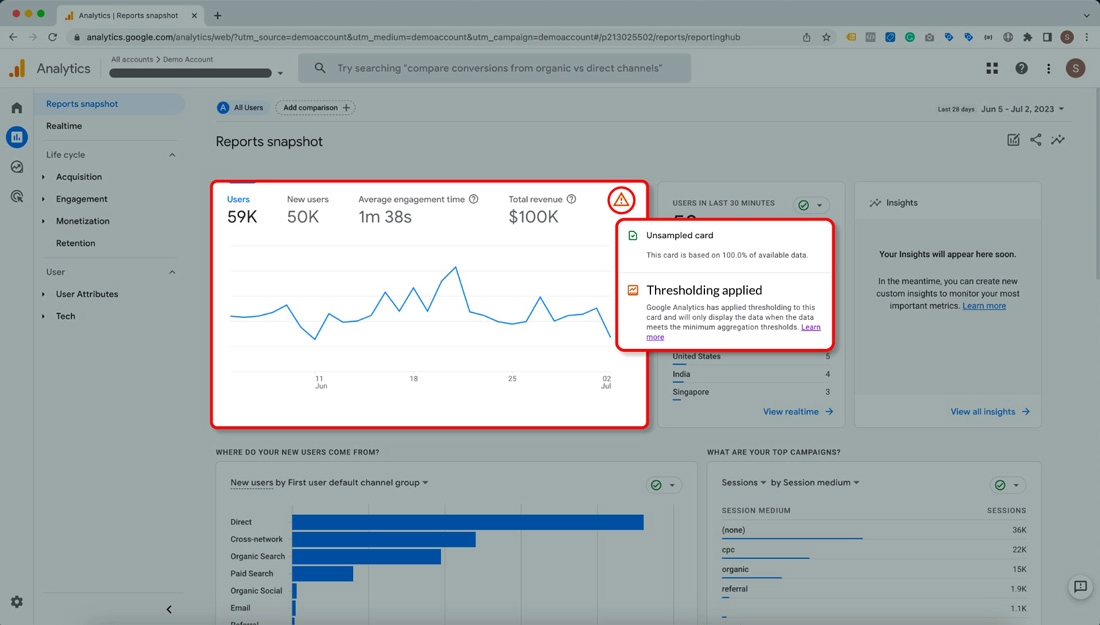
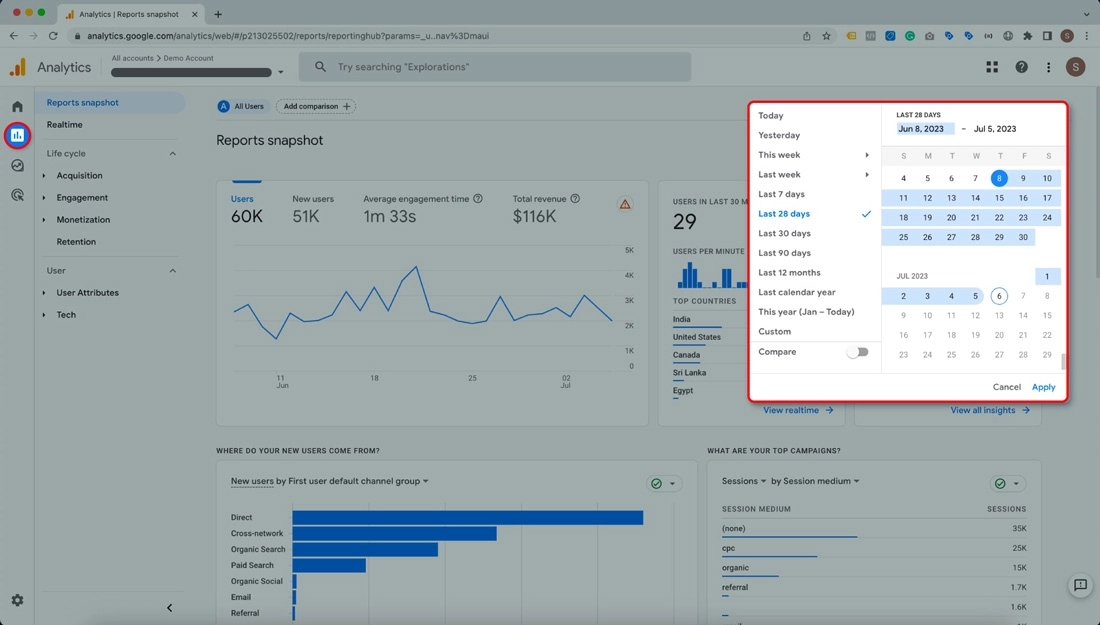
If data thresholding is affecting your reports, there are a few things you can do. Kindly find them below:
Adjust the date range of your report, as a narrow range may trigger data thresholding due to reduced user or event counts.
You may also consider disabling Google Signals if you’re not using the data for remarketing. It will reduce the impact of data thresholding.
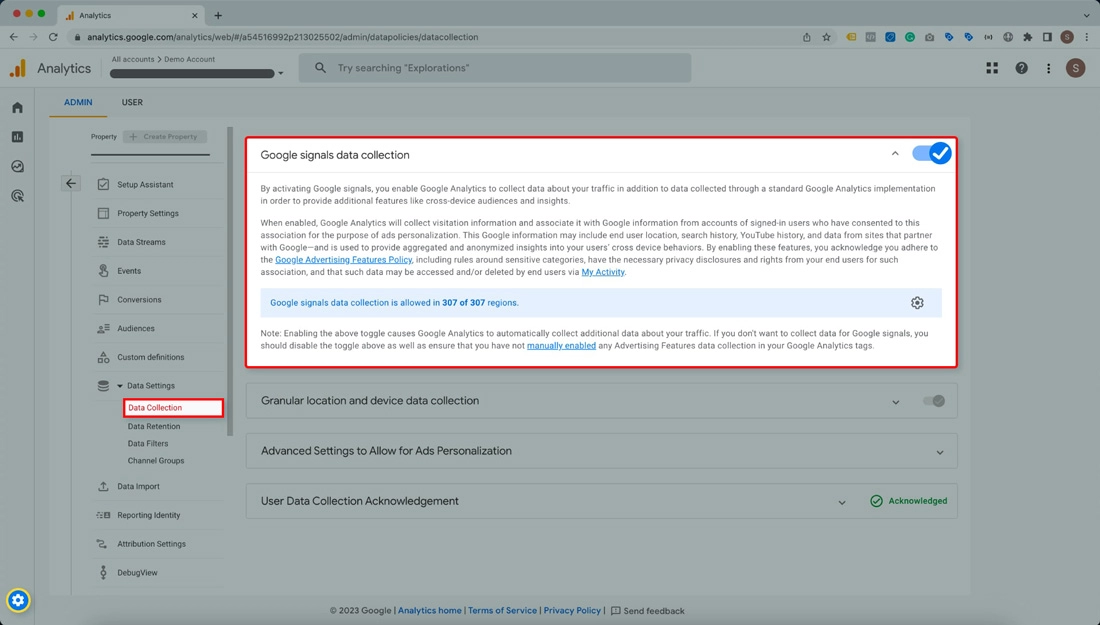
If you wish to continue using Google Signals, you may switch to a device-based reporting identity to reduce the likelihood of data thresholding.
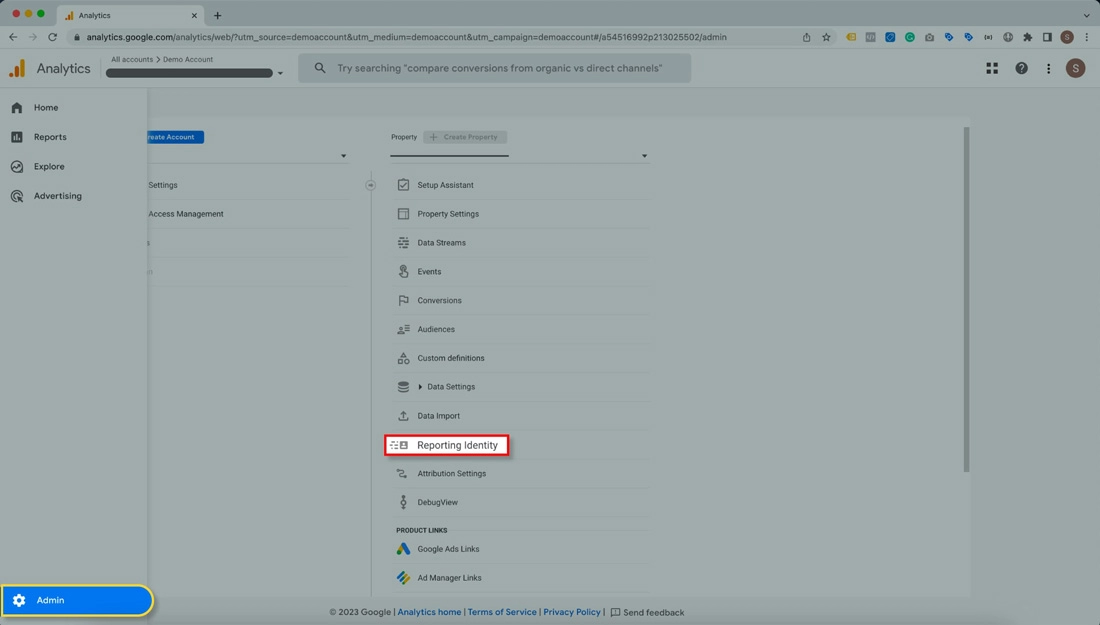
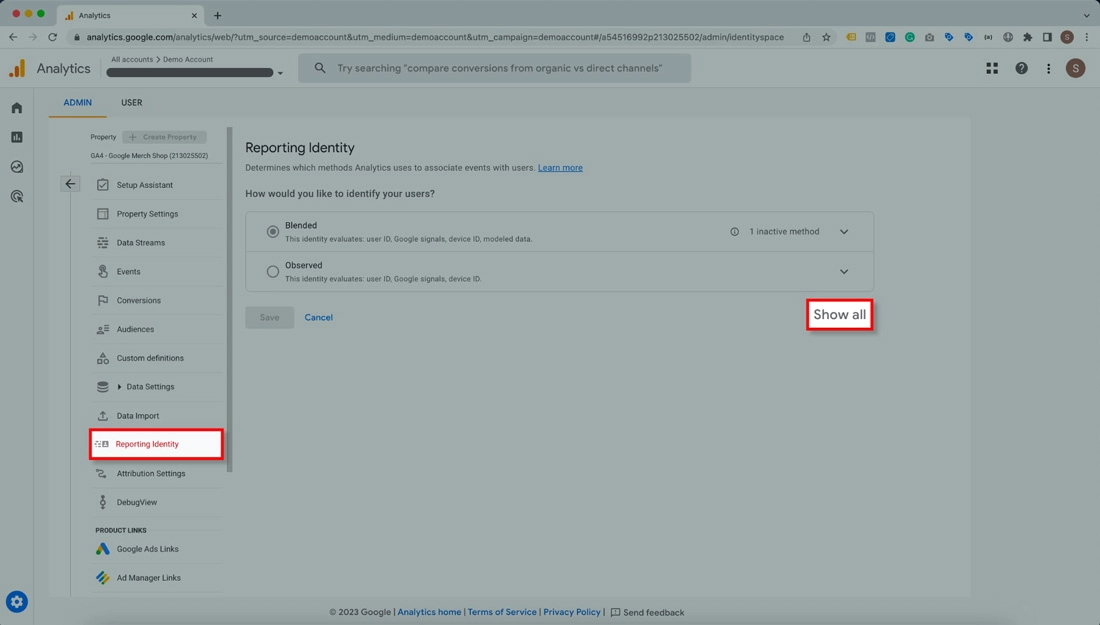
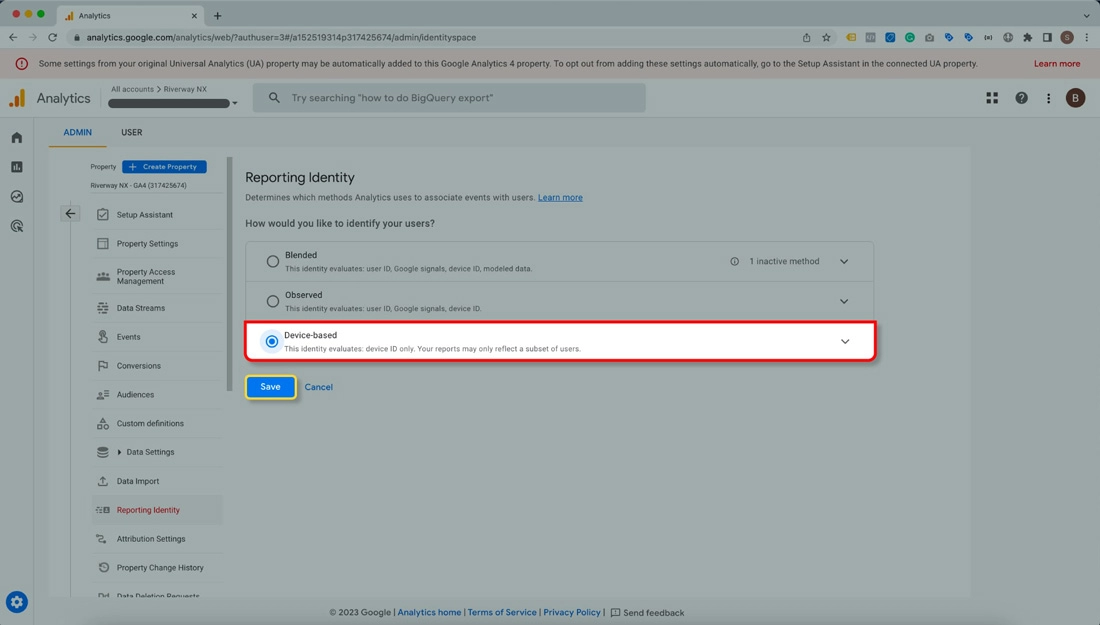
Summarizing the above, we can conclude that Google Analytics 4 is a powerful and flexible tool that allows you to measure and optimize your website performance, user behavior, and marketing campaigns. Google Analytics 4 is a new and evolving platform that offers many benefits and opportunities for web analytics. We are constantly learning and updating ourselves on the latest features and best practices of Google Analytics 4.
Please do not hesitate to reach out to us at support@simprosys.com in case you have any doubts or concerns.
We are always happy to assist you. Thank you for your patience and trust in us!





Leave a Reply